Hybrid inheritance in Java Programming
Before we discuss what is hybrid inheritance, let me answer few of the questions regarding this.
Does java supports hybrid inheritance?
Yes and No. If you are using only classes then this is not allowed in java, however using interfaces it’s possible to have hybrid inheritance in java. We will see this in below example programs.
Hierarchical inheritance and Hybrid inheritance are different?
Yes, Hierarchical inheritance is different than hybrid inheritance. Hierarchical inheritance is possible to have in java even using the classes alone itself as in this type of inheritance two or more classes have the same parent class or in other words a single parent class has two or more child classes, which is quite possible to have in java.
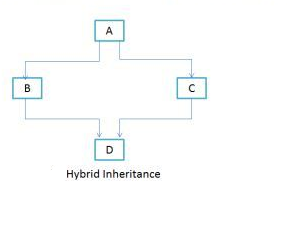
Hybrid Inheritance in Java
As you can see in the above diagram that it’s a combine form of single and multiple inheritance. Since java doesn’t support multiple inheritance, the hybrid inheritance is also not possible.
Case 1:
Using classes: If in above figure B and C are classes then this inheritance is not allowed as a single class cannot extend more than one class (Class D is extending both B and C). Reason explained below!!
Case 2:
Using Interfaces: If B and C are interfaces then the above hybrid inheritance is allowed as a single class can implement any number of interfaces in java.
Let’s understand the above concept with the help of examples:
Example program 1: Using classes to form hybrid
public class A { public void methodA() { System.out.println("Class A methodA"); } } public class B extends A { public void methodA() { System.out.println("Child class B is overriding inherited method A"); } public void methodB() { System.out.println("Class B methodB"); } } public class C extends A { public void methodA() { System.out.println("Child class C is overriding the methodA"); } public void methodC() { System.out.println("Class C methodC"); } } public class D extends B, C { public void methodD() { System.out.println("Class D methodD"); } public static void main(String args[]) { D obj1= new D(); obj1.methodD(); obj1.methodA(); } }
Output:
Error!!
Why? Most of the times you will find the following explanation of above error – Multiple inheritance is not allowed in java so class D cannot extend two classes(B and C). But do you know why it’s not allowed? Let’s look at the above code once again, In the above program class B and C both are extending class A and they both have overridden the methodA(), which they can do as they have extended the class A. But since both have different version of methodA(), compiler is confused which one to call when there has been a call made to methodA() in child class D (child of both B and C, it’s object is allowed to call their methods), this is a ambiguous situation and to avoid it, such kind of scenarios are not allowed in java. In C++ it’s allowed.
What’s the solution? Hybrid inheritance implementation using interfaces.
interface A { public void methodA(); } interface B extends A { public void methodB(); } interface C extends A { public void methodC(); } class D implements B, C { public void methodA() { System.out.println("MethodA"); } public void methodB() { System.out.println("MethodB"); } public void methodC() { System.out.println("MethodC"); } public static void main(String args[]) { D obj1= new D(); obj1.methodA(); obj1.methodB(); obj1.methodC(); } }
Output:
MethodA MethodB MethodC
Note: Even though class D didn’t implement interface “A” still we have to define the methodA() in it. It is because interface B and C extends the interface A.
The above code would work without any issues and that’s how we implemented hybrid inheritance in java using interfaces.

nice blog. java training in chennai
ReplyDeleteWrite more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre talking about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your weblog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
ReplyDeleteconstantly i used to read smaller content which also clear their motive, and that is also happening with this piece of writing which I am reading at this time.
ReplyDeleteNice article thanks for sharing see more about me on my site
ReplyDelete#Multi Level Marketing Software Company in Agra
#Web Design Companies in Agra
#Ecommerce Mobile Application Agra
#Custom Web Application Development - Influx Infotech
#Android Application Development Company in Agra
Thanks and best regards
Gaurav Verma
Influx Infotech
www.influxinfotech.com
☎ +91-7900221133, +91-8909248671