Introducing Class Concept in Java Programming
In the previous article we have learned the basics of class and object related to real life .In this chapter we are going to see the basic programmatic syntax of class.
Syntax : Class
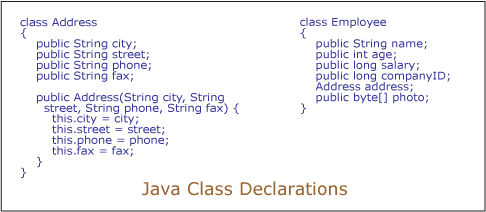
class classname { type instance-variable1; type instance-variable2; // ... type instance-variableN; type methodname1(parameter-list) { // body of method } type methodname2(parameter-list) { // body of method } // ... type methodnameN(parameter-list) { // body of method } }
Explanation Of Syntax
Class name
class classname {
- class is Keyword in Java used to create class in java.
- classname is Name of the User defined Class.
Class Instance Variable
type instance-variable1; type instance-variable2; // ... type instance-variableN;
- Instance Variables are Class Variables of the class.
- When a number of objects are created for the same class, the same copy of instance variable is provided to all.
- Instance variables have different value for different objects.
- Access Specifiers can be applied to instance variable i.e public,private.
- Instance Variable are also called as “Fields“
Class Methods
type methodname1(parameter-list) { // body of method }
- Above syntax is of Class Methods.
- These methods are equivalent to function in C Programming Language.
- Class methods can be declared public or private.
- These methods are meant for operating on class data i.e Class Instance Variables.
- Methods have return type as well as parameter list. We are going to learn this concept deeply in next few tutorials.
Also publish article on Exception....
ReplyDeleteok... i'm adding Exception in further topics ....Lectures are still under construction :)
ReplyDelete